Tropical Rainforest Climate In The Philippines

Regions with this climate are typically designated Af by the Köppen climate classification.
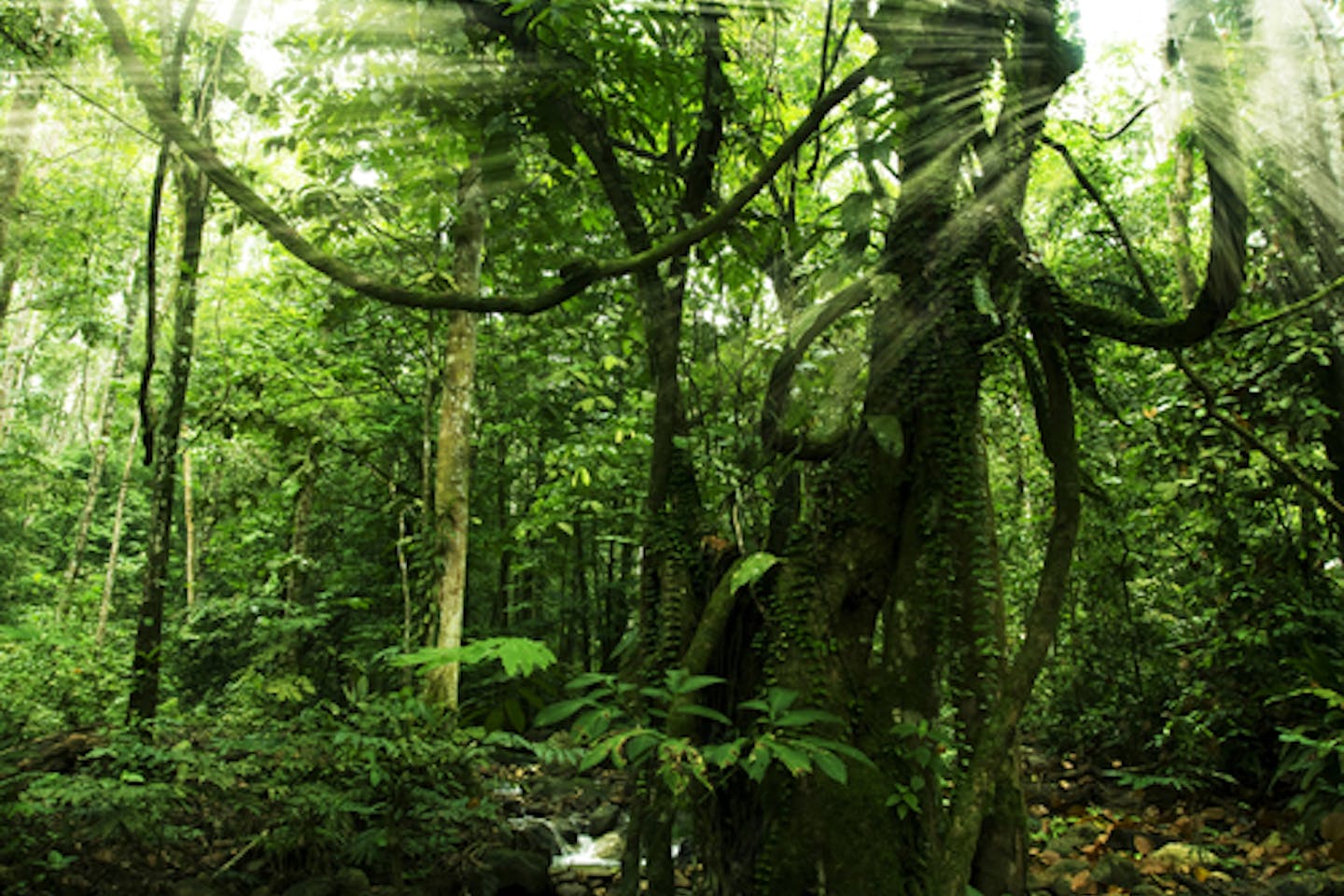
Tropical rainforest climate in the philippines. Each climate is tropical or subtropical in nature due to the Philippine islands proximity to the equator. In the 1920s 60 percent of the land was covered in tropical rainforest. It is known for its dense canopies of vegetation that form three different layers.
Tropical Rainforests are typically located around the equator. Due to this one of their primary characteristics is the hot and wet climate. These forests experience rainfall throughout the year with minimal dry seasons in between.
This includes birds such as the Endangered Green Racquet-tail and at least one breeding pair of the iconic and Critically Endangered Philippine Eagle. Rainfall occurs throughout the year but increases from May to January with an annual average of about 2100 mm. Metro Manila has a tropical savanna climate with dry winters.
The island of Luzon holds the Sierra Madre mountain range which harbors a massive swath of old-growth tropical rainforest home to a wealth of rare species. Tacloban is a city with a significant rainfall. The Luzon Rain Forests ecoregion is classified in the Tropical and Subtropical Moist Broadleaf Forests Biome.
The high rainfall and year-round high temperatures are ideal conditions for vegetation growth. Even in the driest month there is a lot of rain. The rainfall here is around 2220 mm 874 inch per year.
This city has a tropical climate. Over the course of a year the temperature typically varies from 22C in January to 34C in May. The 4 climates The Climate of the Philippines is either tropical rainforest tropical savanna or tropical monsoon or humid subtropical in higher-altitude areas characterized by relatively high temperature oppressive humidity and plenty of rainfall.
















%20-%20John%20Morrison.jpg)