Marine Animals Definition Biology

Marine environments are therefore the most common habitat on Earth.
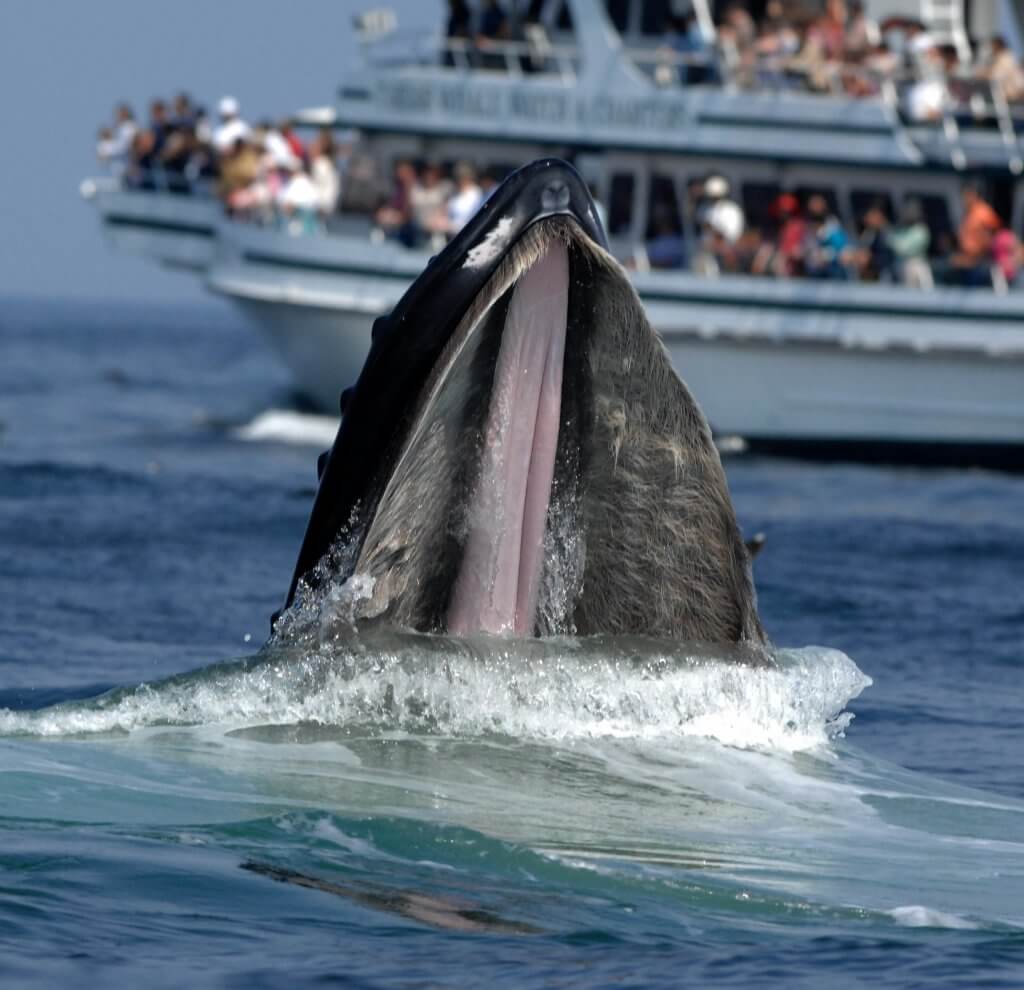
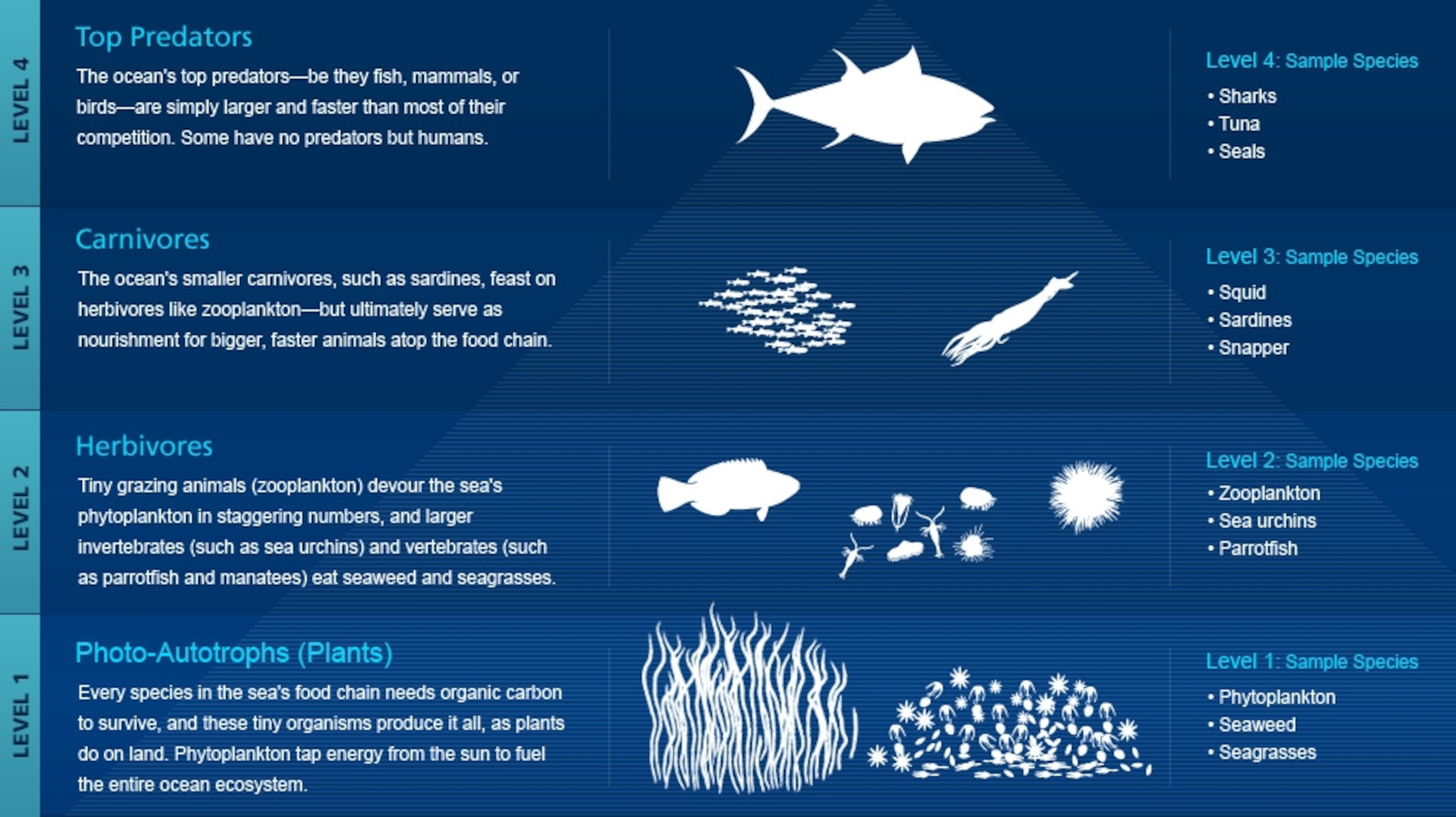
Marine animals definition biology. Marine biology is the scientific study of the biology of marine life organisms in the sea. Archaeocytes- cells that move through the sponge. It also deals with airborne and terrestrial organisms that depend directly upon bodies of salt water for food and other necessities of life.
Osculum- large opening that lets water out. A thin colorless transparent oil that forms a waxy material when it comes into contact with air. An animal belonging to the mammalian order Sirenia which includes manatees and dugongs.
What is Marine Biology. Not only that but water provides a 3-dimensional habitat which increases the available habitat for the animals microbes and plants to live. Marine biology is the scientific study of plants and animals that live in salt water.
There are a vast array of career choices one can pick from - from studying large ocean animals and what they eat to. Spermaceti is found in a cavity in the head of sperm whales. When many people think about a marine biologist they picture a dolphin trainer.
Marine biology the science that deals with animals and plants that live in the sea. Given that in biology many phyla families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land marine biology classifies species based on the environment rather than on taxonomy. So a marine biologist studies.
Marine life definition biology. Spongin- flexible protein fibers. Our ocean coasts and estuaries are home to diverse living things.