Cell Membrane Definition And Function Pdf

Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out.
Cell membrane definition and function pdf. A cell membrane is a border that covers every cell in a living organism. Components of the cell are enclosed in a membrane. Histology places the cellular mechanisms presented in lecture into the context of cell and tissue structure.
Cell Membrane Definition And Function. Histology examines the structure and functions of cells and how cells form tissues and organs. Cell Membrane Composition Functions The cell membrane is also called the plasma membrane and is made of a phospholipid bilayer A.
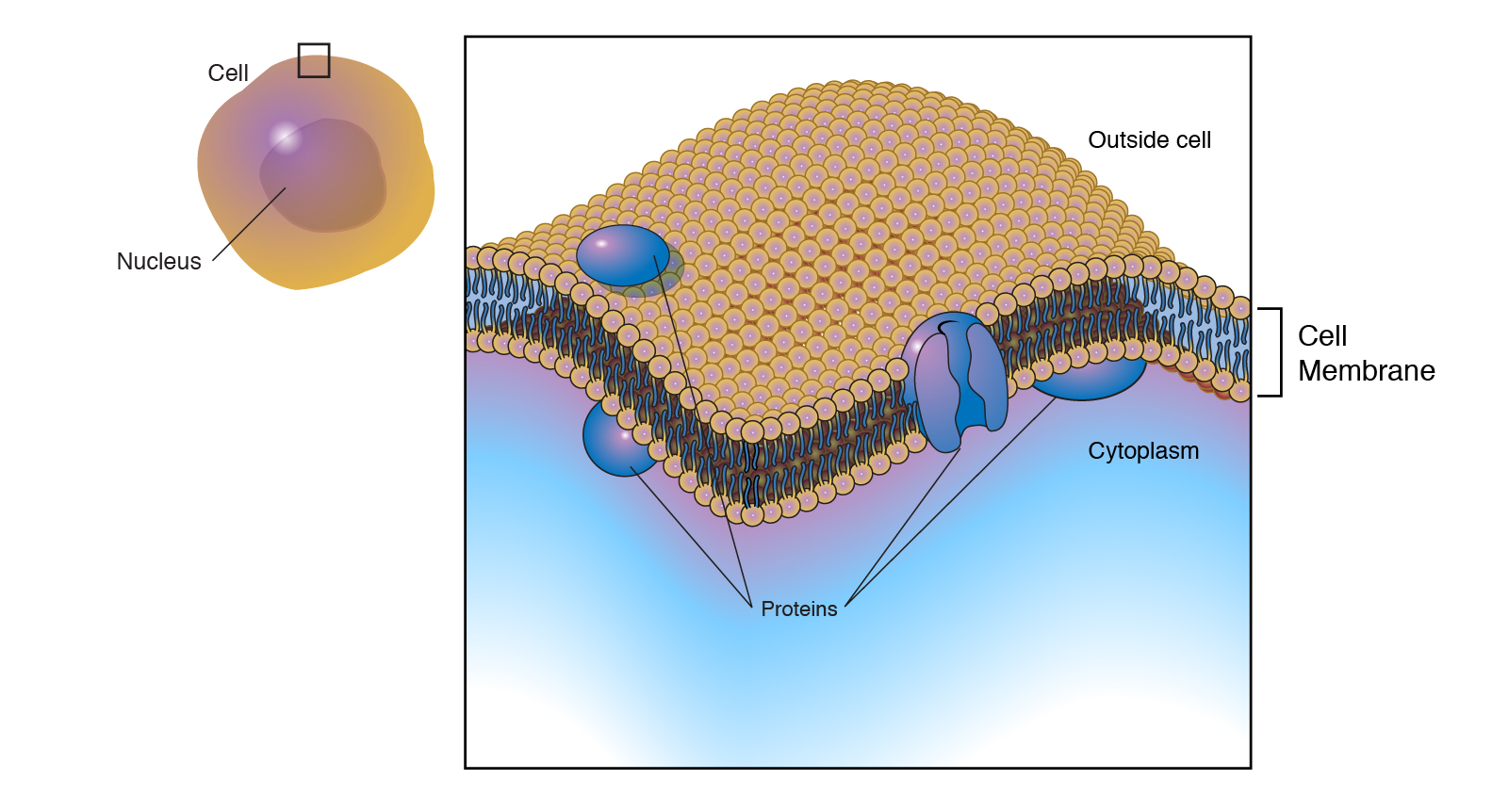
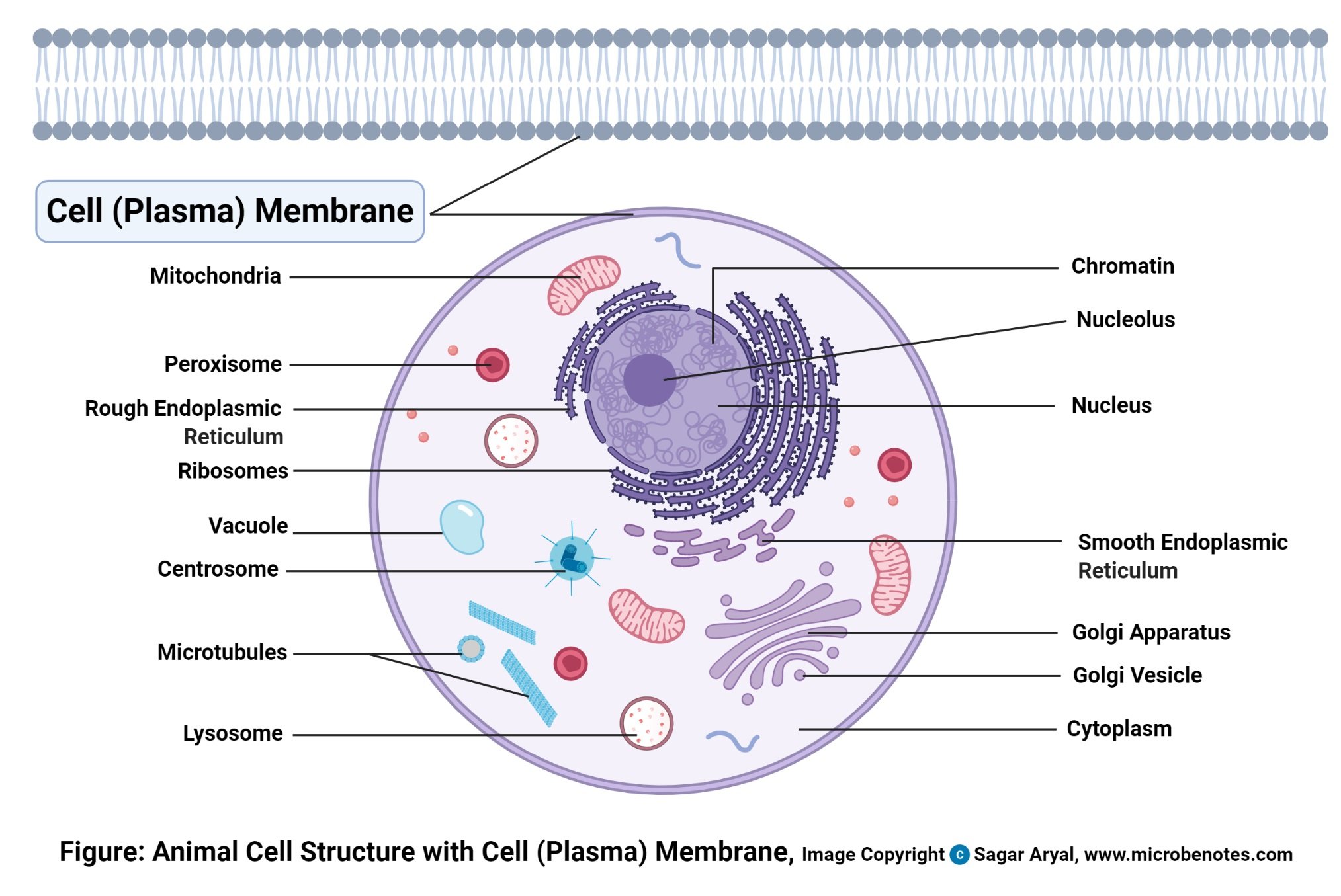
Definition the cell membrane also known as the plasma membrane is a double layer of lipids and proteins that surrounds a cell. It is also known as the cell surface membrane or plasmalemma. Cell membrane are proteins and lipids Membrane proteins and lipids are arranged in a particular fashion both contributing to containing the cell and to selectively allowing or blocking the traffic of certain substances through the cell Such arrangement of molecules provides fluidity.
The plasma membrane is porous and allows the helping to control and coordinate the working of different parts of the body. Its no secret that all living beings on our planet are made up of cells these countless atoms of organic matter. It is a living membrane outermost in animal cells but internal to cell wall in plant cells.
The plasma membrane protects the cell from damage caused by environmental exposure. Unlike Plasma Membrane other organelles do not perform such functions. It is flexible and can fold in as in food vacuoles of Amoeba or fold out as in the formation of pseudopodia of Amoeba Animal cell 1.
The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. Cell Membrane is a boundary of a cell covered with cell walls. The cell membrane functions as a barrier keeping cell constituents in and unwanted substances out and as a gate allowing transport into the cell of essential nutrients and movement from the cell of waste products.














/pinocytosis-594d611e5f9b58f0fc2c5b8f.jpg)
